
In today’s digital landscape, the sophistication and frequency of cyber threats are on a relentless rise, posing an ever-present challenge to organizations across the globe. As these threats evolve, so too must the strategies to counteract them. Among the most innovative and effective strategies emerging in recent years is the Shift Left approach, which seeks to integrate security measures at the earliest stages of the software development lifecycle (SDLC).

This proactive methodology represents a paradigm shift from traditional reactive security measures, aiming to identify and mitigate vulnerabilities well before software products reach production. This article delves into the profound impact of the Shift Left approach on an organization’s cybersecurity posture.
By examining key metrics for evaluation, drawing on real-world examples of success, and analyzing the overarching benefits, we aim to provide a comprehensive overview of how Shift Left not only transforms the development process but also significantly fortifies an organization’s defenses against cyber threats. In doing so, we underscore the importance of adopting Shift Left as not merely a set of practices but as a foundational principle that embeds security into the DNA of software development, ensuring that cybersecurity is not an afterthought but a cornerstone of technological innovation and deployment.
Understanding the Shift Left Approach
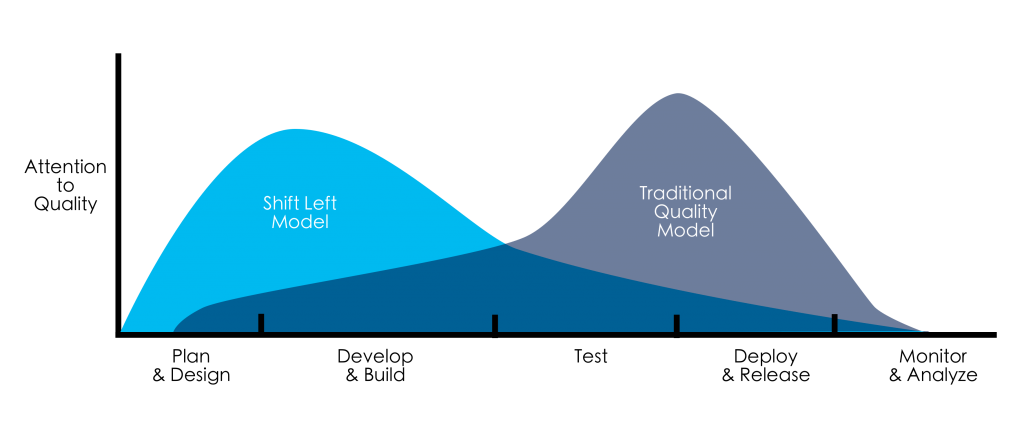
The Shift Left approach is a transformative strategy in the realm of software development and cybersecurity. By integrating security considerations early in the software development lifecycle (SDLC), organizations aim to preemptively identify and mitigate potential vulnerabilities, thereby enhancing their cybersecurity posture from the ground up. This section explores the core principles of Shift Left, its rationale in the context of cybersecurity, and the intrinsic benefits it offers to organizations navigating the complex landscape of digital threats.
Definition and Principles of Shift Left
Shift Left is predicated on the notion that security should be a primary consideration throughout the entire SDLC, not just a final checkpoint before deployment. This approach involves the integration of security practices and testing in the earliest phases of software design and development. Key principles include continuous integration and testing, proactive vulnerability assessment, and the inclusion of security as a fundamental aspect of software quality.
Rationale Behind Shift Left for Cybersecurity
The rationale for adopting Shift Left in cybersecurity is compelling. Traditional security practices often involve conducting security assessments and testing after the development process is nearly complete. This can lead to the identification of vulnerabilities at a stage when they are more difficult and costly to address. In contrast, Shift Left seeks to identify these vulnerabilities much earlier when they are easier and less expensive to fix. This early intervention is critical in today’s fast-paced digital environment, where the speed of development can often outpace security considerations, leaving systems exposed to exploitation.
Benefits of Shift Left for Cybersecurity
Early Vulnerability Detection: By focusing on security from the outset, organizations can detect vulnerabilities at the earliest possible stage. This not only reduces the risk of security breaches but also minimizes the potential impact of such vulnerabilities on the final product.
Enhanced Security Culture: Shift Left fosters a culture where security is everyone’s responsibility, not just that of a dedicated security team. This cultural shift ensures that security considerations are woven into the fabric of the development process, leading to more secure outcomes.
Cost-Effective Security Practices: Identifying and addressing vulnerabilities early is significantly less costly than remedying them post-deployment. This cost-effectiveness extends beyond financial savings, encompassing time and resources that can be reallocated to innovation and development.
Improved Compliance and Trust: Early security integration helps ensure that software products comply with regulatory standards and industry best practices from the beginning. This compliance not only mitigates the risk of legal and financial penalties but also enhances trust among customers and stakeholders.
Faster Time to Market: By reducing the incidence of late-stage security issues, Shift Left can streamline the development process, enabling faster time to market for new products and features. This speed does not come at the expense of security but rather is facilitated by the proactive integration of security measures.
Implementing Shift Left: A Strategic Overview
The implementation of Shift Left involves several key strategies, including the adoption of security automation tools, the development of secure coding practices, and the establishment of cross-functional teams that include security expertise. Training and awareness programs are also critical, ensuring that all team members understand their role in maintaining security throughout the SDLC.
In essence, the Shift Left approach represents a fundamental rethinking of how security is integrated into software development. By prioritizing security from the earliest stages of project conception and design, organizations can significantly enhance their cybersecurity posture, reduce the risk of breaches, and build software that is secure by design. This proactive stance on security is not only a technical necessity but also a strategic advantage in the increasingly complex and threat-prone digital landscape.
Metrics for Measuring the Impact of Shift Left
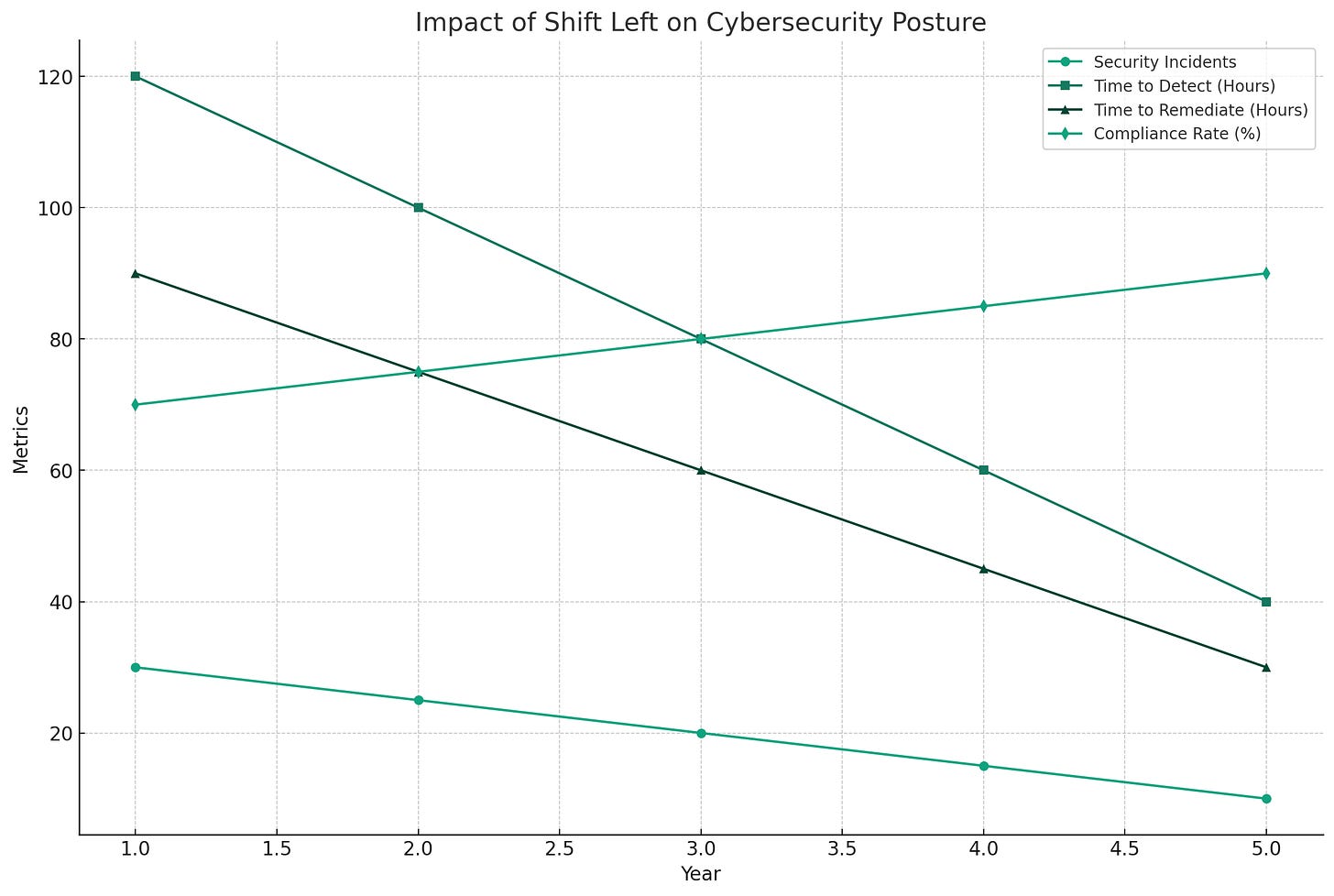
To gauge the efficacy of the Shift Left strategy in fortifying an organization’s cybersecurity posture, it’s essential to analyze specific metrics. These indicators offer concrete evidence of how preemptive security measures can positively influence the security integrity of software products and systems. This section delves into pivotal metrics such as the reduction in post-deployment vulnerabilities, the expedited remediation of vulnerabilities, the financial benefits stemming from mitigated security incidents, and the enhancement of compliance with established security standards.
Reduction in Vulnerabilities Detected Post-Deployment
A direct indicator of Shift Left’s effectiveness is the noticeable decrease in vulnerabilities discovered after the deployment phase. This metric reflects the success of early-stage security testing and vulnerability management in preemptively identifying and resolving potential security threats. For instance, an e-commerce platform implementing Shift Left practices reported a 40% drop in critical vulnerabilities detected in production over a single year, showcasing the method’s significant impact on improving software security.
Time to Remediate Vulnerabilities
Another critical metric is the duration required to address vulnerabilities, showcasing the efficiency and agility of an organization’s security protocols. Shift Left aims to substantially shorten this timeframe by early identification of vulnerabilities when they are generally simpler to fix. A notable observation from a financial services firm revealed a 50% reduction in their average vulnerability remediation time post-Shift Left adoption, highlighting the strategy’s role in enhancing the responsiveness of security operations.
Cost Savings on Security Incident Mitigation
The Shift Left approach can also lead to considerable cost savings by averting security breaches that necessitate costly remedial actions. Evaluating the financial impact of Shift Left through the lens of reduced expenses related to post-deployment security incidents can underscore the cost-effectiveness of proactive security engagements. A software development company, for example, managed to sidestep a potential security breach through Shift Left strategies, saving millions in potential mitigation costs, data recovery efforts, and associated legal fees, thus exemplifying the financial prudence of early security integration.
Improvement in Compliance with Security Standards
Furthermore, Shift Left can elevate an organization’s adherence to regulatory security standards and protocols, a metric indicative of the strategy’s contribution towards maintaining stringent security governance and minimizing non-compliance risks. A healthcare technology company’s transition to Shift Left practices led to achieving 100% compliance with HIPAA security mandates during their subsequent audit, a significant improvement from 75% compliance the year prior. This enhancement not only underscores Shift Left’s role in cultivating a compliance-centric and security-first culture but also its effectiveness in navigating the complex landscape of industry-specific regulatory requirements.
By closely monitoring these metrics, organizations can obtain insightful feedback on the success of their Shift Left initiatives, enabling data-driven adjustments that continually refine and bolster their cybersecurity stance. The improvements seen across these metrics not only validate the tangible benefits derived from the Shift Left approach but also emphasize the critical importance of weaving security considerations seamlessly into every phase of the software development lifecycle to achieve a resilient cybersecurity posture.
Overcoming Challenges in Implementing Shift Left
While the Shift Left approach significantly enhances an organization’s cybersecurity posture, implementing it comes with its set of challenges. These include bridging the skills and knowledge gaps within teams, integrating security practices into existing workflows without hampering productivity, and maintaining the speed of development alongside rigorous security testing. Addressing these challenges head-on is crucial for organizations to fully leverage the benefits of Shift Left.
Skills and Knowledge Gaps
A fundamental challenge in adopting Shift Left is ensuring that development teams possess the necessary security skills and knowledge. For example, a digital marketing agency confronted this challenge by developing a custom training program focused on secure coding practices and the effective use of security testing tools. This initiative not only equipped their developers with the essential skills but also fostered a proactive security mindset across the organization.
Integrating Security into Existing Workflows
Another significant hurdle is the seamless integration of security practices into established development workflows. A software development company managed to overcome this by adopting a phased approach to tool integration, starting with non-intrusive security tools and gradually increasing their complexity. This strategy minimized disruption and facilitated a smoother transition to a security-integrated development process.
Maintaining Development Speed While Ensuring Security
Balancing the need for rapid development with comprehensive security testing presents a challenge. An IT services firm addressed this by implementing automated security testing and adopting a risk-based approach to prioritize testing efforts. This allowed them to maintain their development velocity while ensuring that critical security issues were identified and addressed promptly.
Learn How To Build AI Projects
Learn How To Build AI Projects
Now, if you are interested in upskilling in 2024 with AI development, check out this 6 AI advanced projects with Golang where you will learn about building with AI and getting the best knowledge there is currently. Here’s the link.
Conclusion
The Shift Left approach represents a paradigm shift in how organizations address cybersecurity, emphasizing the early integration of security measures in the software development lifecycle. By adopting Shift Left, organizations can achieve a marked reduction in vulnerabilities, expedite the remediation process, realize cost savings from mitigated security incidents, and enhance compliance with security standards. The tangible benefits observed through key metrics underscore the effectiveness of Shift Left in bolstering an organization’s cybersecurity posture.
However, the successful implementation of Shift Left is not without its challenges. Overcoming skills and knowledge gaps, integrating security into existing workflows, and balancing development speed with security rigor are critical hurdles that organizations must navigate. Through strategic initiatives such as targeted training programs, phased tool integration, and the adoption of automated testing and risk prioritization, these challenges can be addressed, enabling organizations to fully realize the benefits of Shift Left.
In conclusion, while implementing Shift Left requires a concerted effort to overcome inherent challenges, the payoff in enhanced cybersecurity posture is undeniable. Organizations are encouraged to view Shift Left not just as a set of practices but as a fundamental cultural shift towards prioritizing security at every stage of software development. As cyber threats continue to evolve, adopting a proactive stance through Shift Left offers a robust strategy for organizations to protect their digital assets and ensure the security and reliability of their software products.
